AI affordance understanding
RECOG AI Robust Evaluation of Cognitive Capabilities and Generality in Artificial Intelligence.
The background of this project lies in meeting the need for validity in evaluation of AI cognitive capabilities, such as object permanence and affordance understanding. The current lack of validity generates a large disparity between the “hype” of AI achievement and the reality, and contributes to a feeling of distrust about what AI is really capable of. It also makes it difficult to predict the potential operational applications of AI in the future. This project takes a new approach to AI evaluation and benchmarking, drawing inspiration from cognitive science. It developed a novel conceptual and methodological framework for evaluating AI capabilities that offers consistency, comprehensiveness, and robustness. The primary objective is to create a robust evaluation framework and benchmarking system capable of assessing AI’s cognitive capabilities both in the present and in the long term. The overarching goal is to establish a methodology that can be adopted by others to assess the robustness of cognitive capabilities in artificial systems.
More specifically, (from the project website) the methodology draw from cognitive psychology and psychometrics to translate well defined cognitive capabilities (such as “object permanence”) into skills (e.g. “find an occluded reward”), and then into individual tests, and varied instances (varying in surface features) of these tests. The aim is to facilitate the robust conclusion that an individual “has” or “does not have” a capability, based on their pattern of performance across a battery of tests and instances. The second is a protocol to assimilate existing AI benchmarks into the framework so that performance on these established assessments can be interpreted in terms of capabilities. This way we can better understand existing AI progress in terms of cognitive capabilities. This will require understanding the relationship between the actual and intended requirements of these benchmarks, and how they can be related to the skills afforded by specific capabilities. Final part is the design of an innovative benchmark for evaluating cognition in AI within a 3D environment. This is based on the existing benchmark AnimalAI, adapted to incorporate new features required by the evaluation framework designed in the rest of the project. Details of the Animal AI platform and its latest developments can be found at Github. You can learn about, play, and watch AI performance on the old version at the website.
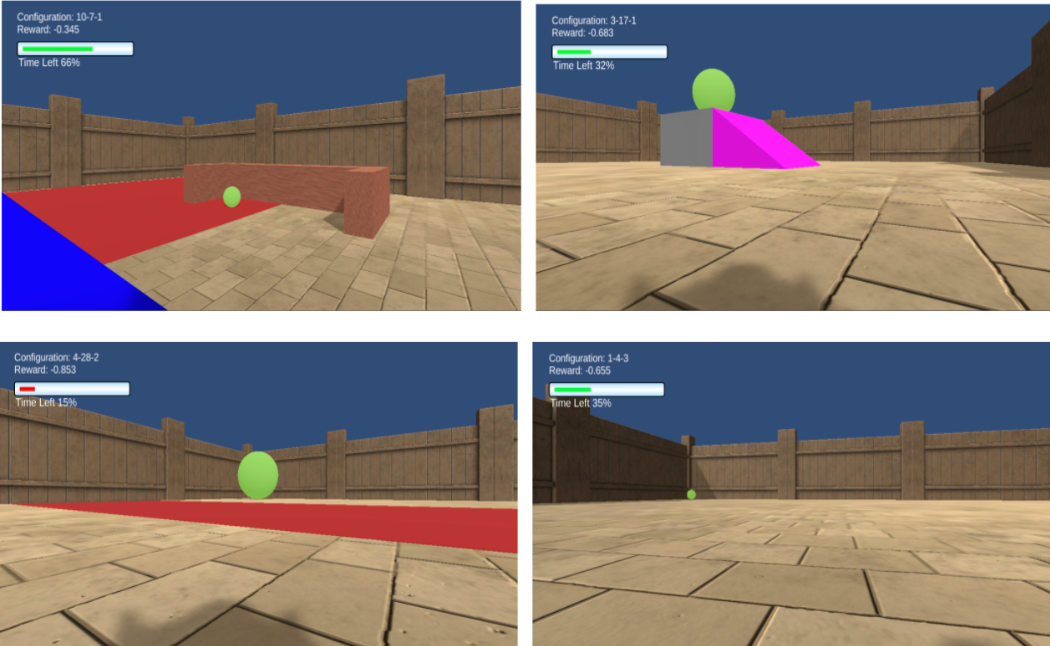
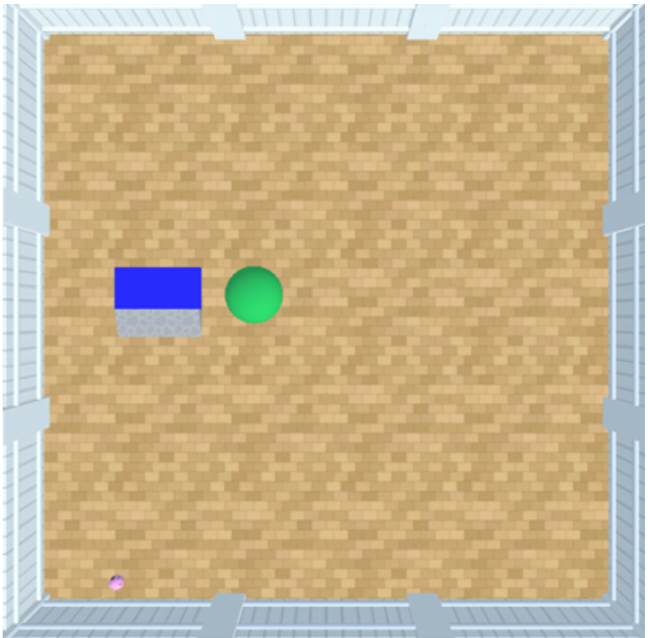
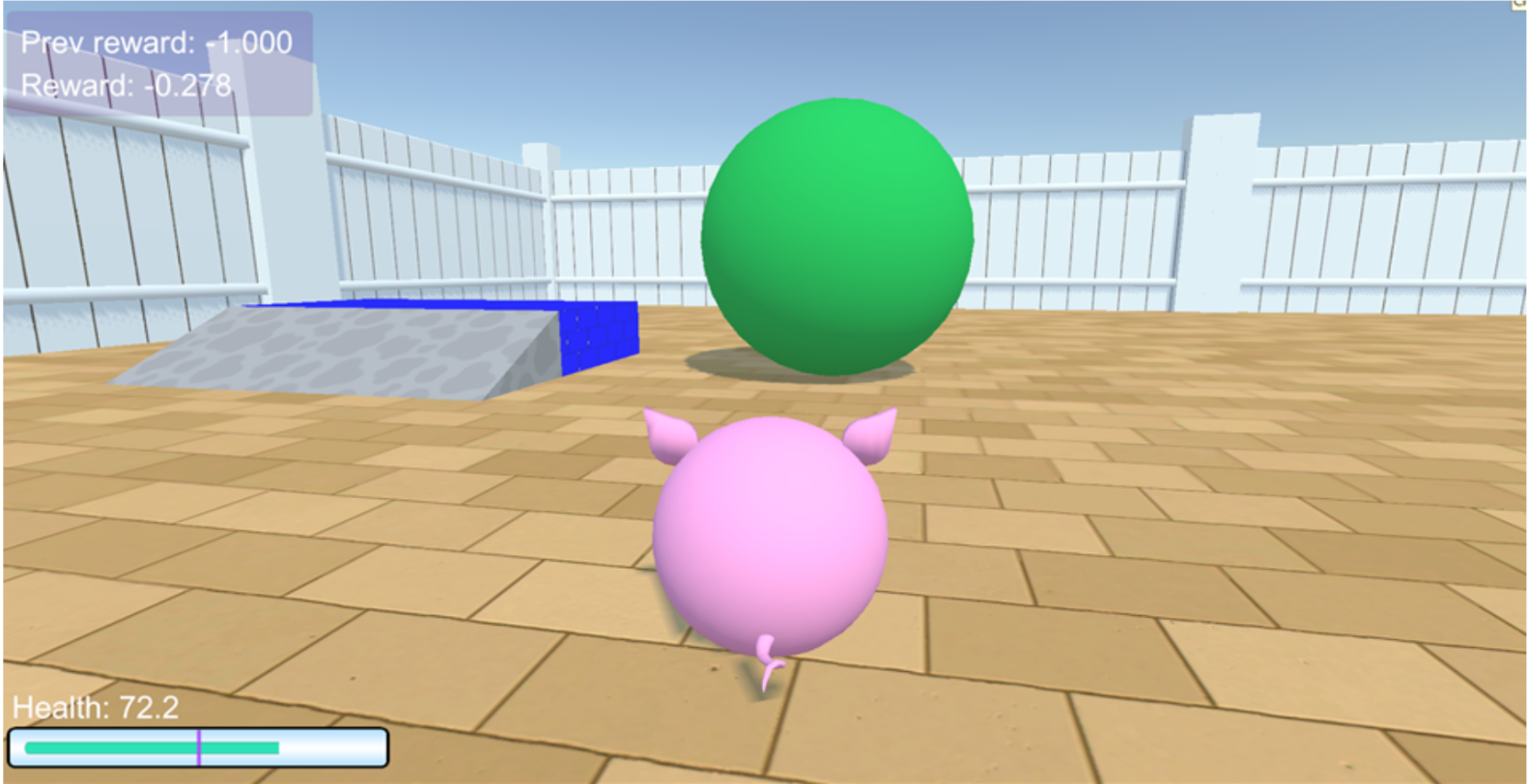
I mainly helped with development and design of a suite of tasks (well controlled cognitive tests) for AI affordance understanding. Affordances are action possibilities that are formed based on the relationship between an agent and the environment, as well as objects in that environment, in which the agent is situated. We adopted a interactive approach to evaluate and benchmark affordance understanding, because accounting for learning and interaction specifically captures crucial facets of the theory behind affordances. The suite of tasks were developed and built in the AnimalAI game engine simulator in Unity and different reinforcement learning agents are trained in the simulated environment by a training Python API. I was also part of procedurally generate a large collection of variations of tasks in each sub-suite.
References
2024
- GIBSONA: General Interaction Battery: Simple Object Navigation and AffordancesSSRN Preprint, 2024